
The estimated activity base can be direct labor hours, machine hours, or any other cost driver relevant to the business. Until now, you have payroll learned to apply overhead to production based on a predetermined overhead rate typically using an activity base. An activity base is considered to be a primary driver of overhead costs, and traditionally, direct labor hours or machine hours were used for it. For example, a production facility that is fairly labor intensive would likely determine that the more labor hours worked, the higher the overhead will be.
Recap of Three Allocation Methods
In order to calculate the predetermined overhead rate for the coming period, the total manufacturing costs of $400,000 is divided by the estimated 20,000 direct labor hours. For example, the total direct labor hours estimated for the solo product is 350,000 direct labor hours. With $2.00 Accounting for Technology Companies of overhead per direct hour, the Solo product is estimated to have $700,000 of overhead applied.
- Costs to heat and cool a building will vary depending on the time of year, and it is possible that materials costs can increase or decrease during the year depending on the type of product being produced.
- In order to calculate the predetermined overhead rate for the coming period, the total manufacturing costs of $400,000 is divided by the estimated 20,000 direct labor hours.
- Applying our formula, we get $188,000 in fixed overhead divided by the base of 18,800 total direct labor hours for an allocation rate of $10 per labor hour.
- For example, if we choose the labor hours to be the basis then we will multiply the rate by the direct labor hours in each task during the manufacturing process.
- The production head wants to calculate a predetermined overhead rate, as that is the main cost allocated to the new product VXM.
Managerial Accounting
The cost information provided by ABC isgenerally regarded as more accurate than the information providedby most traditional costing methods. This allows management to makebetter decisions in areas such as product pricing, product linechanges (adding products or eliminating products), and product mixdecisions (how much of each product to produce and sell). You can see from this analysis that the Deluxe boat consumesfour times the machine hours of the Basic boat. At a rate of $30per machine hour, the Deluxe boat is assigned $1,200 per boat forthis activity ($30 rate × 40 machine hours) while the Basic boat isassigned $300 per boat ($30 rate × 10 machine hours). This formula applies to all indirect costs, whether manufacturing overhead, administrative costs, distribution costs, selling costs, or any other indirect cost. Therefore, this predetermined overhead rate of 250 is used in the pricing of the new product.

Determining Estimated Overhead Cost
- That amount is added to the cost of the job, and the amount in the manufacturing overhead account is reduced by the same amount.
- If the actual overhead at the end of the accounting period is 1,575 the overhead is said to be under applied by 125 (1,450 – 1,575).
- However, the production manager wants to see if there are other, more rational ways to allocate overhead that take into account the longer and more intense production time and energy to produce the deluxe purse.
- The formula for a predetermined overhead rate is expressed as a ratio of the estimated amount of manufacturing overhead to be incurred in a period to the estimated activity base for the period.
- The estimated activity base can be direct labor hours, machine hours, or any other cost driver relevant to the business.
One of the advantages of predetermined overhead rate predetermined overhead rate is that it can help businesses monitor overhead rate. A business can calculate its actual costs periodically and then compare that to the predetermined overhead rate in order to monitor expenses throughout the year or see how on-target their original estimate was. This comparison can be used to monitor or predict expenses for the next project (or fiscal year). The use of such a rate enables an enterprise to determine the approximate total cost of each job when completed. In recent years increased automation in manufacturing operations has resulted in a trend towards machine hours as the activity base in the calculation. In these situations, a direct cost (labor) has been replaced by an overhead cost (e.g., depreciation on equipment).
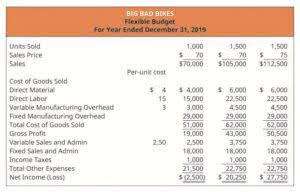
The manufacturing overhead costs are applied to the product based on the actual number of activity base units used during the accounting period. High Challenge Company allocated manufacturing overhead costs to the two products for the month of January. Sales of each product have been strong, and the total gross profit for each product is shown in Figure 6.7.
- Companies that produce several different products may believethat the benefits of implementing ABC will outweigh the costs.However, management must be willing to use the ABC information tobenefit the company.
- In this article, we will discuss the formula for predetermined overhead rate and how to calculate it.
- That is, if the predetermined overhead rate turns out to be inaccurate and the sales and production decisions are made based on this rate, then the decisions will be faulty.
- Albert Shoes Company calculates its predetermined overhead rate on the basis of annual direct labor hours.
- This is calculated at the start of the accounting period and applied to production to facilitate determining a standard cost for a product.
